- RACING FLAG
- A special flag flown from a yacht that is taking part in a race, and struck
if it withdraws or when it crosses the finish line (see also
prize flag and
strike).
- RADIANT
- (adj) The heraldic term for rays that expand from a central point, but
which may also be applied to other charges and to ordinaries that are
similarly arranged rayonnι or rayonnant - but see
radiated (also
gyronny,
ordinary and
radiating).


Flag and Arms of Zakliczyn, Poland (Jarig Bakker)
Please note that the vexillogical term for rays spreading out from a central
point is radiating see radiating 1).
- RADIATED
- (adj) A heraldic term used when rays are seen issuing from a charge for example the Madonna radiated
as shown below but see radiant (also radiating and
sun-in-splendour).



Arms of Glogσw. Poland (Jarig Bakker); Flag of uto Orizari, Macedonia (fotw); Flag of Ferden, Switzerland (fotw)
- RADIATING
- 1) (adj) Rays spreading out from a central point and widening towards the
edge of a flag as in, for example, the naval ensign of Japan, or the flag of the
US State of Arizona (see also active,
inactive and radiant, radiated,
sunburst, and compare with
gyronny).
- 2) (adj) A stripe or stripes usually widening from one fixed point, but occasionally
from two closely spaced points as in, for example, the flags of the
Marshall Islands or the Seychelles.
- 3) (adj) A group of objects or charges placed in an arc (usually from one fixed point)
as in the national flags of China and Adygea.
![[radiating flags]](../images/v/vxt-d263.gif)
![[radiating flags]](../images/v/vxt-d263a.gif)
![[radiating flags]](../images/v/vxt-d263b.gif)
From left: Flag of Arizona, USA (fotw); National Flag of the Seychelles (fotw); Naval Ensign of Japan
![[radiating flags]](../images/v/vxt-d263c.gif)
![[radiating flags]](../images/v/vxt-d263d.gif)
National Flag of China (fotw); National Flag of Adygea, Russia (CS)
Please note with regard to 1) that the heraldic term for rays spreading out from a central point is radiant
see radiant.
- RAGGED CROSS
- See raguly.
- RAGULY
- A heraldic term meaning any number of small regular projections set an angle
on both sides of a bar, cross or saltire and thought to represent a roughly trimmed
branch as in, for example, the ragged cross (more accurately saltire) of Burgundy
and later Spain.


Spanish Naval Flag 16-17th C (fotw); Flag of Riedern, Switzerland (fotw)
- RAINBOW COLOURS (or COLORS)
- See dressing lines (also
dress ship).
- RAINBOW FLAG
- 1) One of several flags showing the colours of the rainbow, with two prominent examples being the gay pride flag
illustrated below and that of the Italian peace movement illustrated under peace flag.
- 2) An unofficial nickname for the national flag of South Africa.
![[Federal Service Flag of Germany]](../images/v/vxt-d411.gif)
From left: The Current Gay Rights Flag; The Flag of Cusco, Peru (fotw)
- RAISED
- 1) The act of having displayed a flag.
- 2) See enhanced
- RAMPANT
- See Appendix V.
- RANGE FLAG
- One of the signal flags used on target ranges (such a red warning flag)
used to signal safe or dangerous conditions (see also red flag 1)).
- RANK FLAG
- 1) A flag which signifies the rank of a military officer as opposed to that
of a civilian functionary - but please see also
flag of command,
individual flag and
tugh (also
flag officer 3),
in abeyance and
rank plate).
- 2) An alternative term for a distinguishing flag (see
distinguishing flag).
![[rank flags]](../images/v/vxt-d267.gif)
From left: France - General, Lieutenant General, Major General, Brigadier General
(FOTW)
Please note, that although these terms are sometimes
considered interchangeable, the Editors have drawn a general distinction between
the command flags used by senior naval officers, the rank flags employed by officers
from the other armed services, the distinguishing flags of civilians and with
personal flags.
- RANK PLATE
- In UK, US and some other usage, a rectangular panel that is displayed on the vehicle
carrying a senior officer of the armed services, and used in place of or in addition to
their relevant rank flag or flag of command an automobile, distinguishing, star
or plate
(see also car flag,
flag of command 1),
flag officer 3),
flag disc and rank flag 1)).
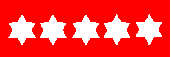

From left: Field Marshall UK and Five Star General Army and Marine Corps US (CS)

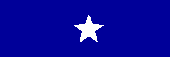
From left: Commodore Royal Navy and Brigadier Royal Marines UK, Rear Admiral (Lower Half) USN and Brig Gen USAF (CS)
Please note that the number of stars range between one and five
dependent upon the rank of the officer concerned.
Please note also that in US service officers of the army and the
Marine Corps have red plates, whilst those of the USN and USAF have dark blue. In UK service,
however, officers of the army have red, of the RN and Royal Marines dark blue, and of the
RAF light blue (and that there is a combined services plate whose field is of vertical
stripes in dark blue, red and light blue).
- RATIO
- See proportions.
- RAVEN FLAG
- The flag considered by some sources to have been carried by Viking raiding
parties up until the 11th Century, and to have been carried by the Normans at
the Battle of Hastings (1066).
![[Raven flag]](../images/v/vxt-d269.gif)
(fotw)
- RAYONNΙ (or RAYONNANT)
- See radiant.
- RECONSTRUCTION
- A term for the image of a (largely but not exclusively) historical flag that is based upon written sources only.
- RECTANGLE (or RECTANGULAR)
- A figure composed of four right angles so having its opposite sides parallel but see note
below (also dimensions).




Please note that this term is sometimes used to exclude a square that is a figure with proportions
of 1:1 - especially when different ratios are being compared see proportions.
- RED CROSS (CRESCENT or DIAMOND) FLAG
- See safe conduct flag (also
Geneva Convention flag).
- RED DUSTER
- An affectionate nickname for the British civil ensign (see also red ensign
below).
- RED ENSIGN
- 1) In English then British usage the ensign ensign usually (but not invariably)
now worn undefaced by all privately owned merchant vessels and
yachts the red duster (see also armorial ensign,
civil ensign under 'ensign'
blue ensign,
gridiron flag,
undefaced) and
white ensign.
- 2) Generically, any canton flag (either plain or defaced) with a red field particularly
(but not exclusively) if flown at sea a British-style ensign (see also
canton flag 1),
blue ensign 2) and
deface).
![[British Red Ensign]](../images/v/vxt-d270.gif)
![[British Red Ensign]](../images/v/vxt-d270a.gif)
![[British Red Ensign]](../images/v/vxt-d270b.gif)


From left: Red Ensigns, England c16251707; UK 17071801(CS); UK From 1801 UK From 1801 and Civil Ensign from 1864 (fotw);
Civil Ensign of Ghana; Civil Ensign of Nigeria (fotw)
Please note with regard to 1) that the red ensign is flown defaced by a few yacht
clubs and by some non-governmental bodies (see also defaced)
![[Royal Dart Yacht Club]](../images/v/vxt-d270c.gif)
Royal Dart Yacht Club, UK (fotw)
- RED FLAG
- 1) A plain red flag used in a variety of circumstances to signify danger (see also
beach flag,
fire alert flag,
range flag and
storm warning flags).
- 2) The colloquial term for a predominantly or wholly red flag signifying revolution the bloody flag.
- 3) A colloquial term for the national flag of the former Soviet Union
(see also banner of victory 1)).
- 4) See flag of defiance.
With regard to 1) please note that the International Code of Signals
stipulates flag bravo a plain red swallow tail should be flown when loading, discharging or
carrying a dangerous cargo (see also
international code of signals and
swallow tail(ed)).
Please note with regard to 2) that the first recorded use of such a flag (with political motives)
was when it was flown by some ships during the mutiny at the Nore in the Royal Navy of 1797 and
thereafter during several revolutionary situations until becoming firmly associated with Socialism
during the Paris Commune of 1871. This red flag was the direct ancestor of the later Soviet and
other Communist flags - see 'red flag 3)' above.
![[Danger flag, Flag Bravo and Soviet Union]](../images/v/vxt-d1701.gif)
From left: Danger Flag (CS); Flag Bravo (CS); National Flag of The Soviet Union 1924 1991 (fotw)
- REDUCED BEND
- See west-east diagonal
(also ascending diagonal,
bend in Appendix VI,
descending diagonal,
'east-west diagonal',
north-south diagonal and
south-north diagonal).
![[reduced bend flag]](../images/v/vxt-d271.gif)
- REDUCED BEND SINISTER
- See east-west diagonal (also
ascending diagonal,
bend sinister in Appendix VI,
descending diagonal,
north-south diagonal,
south-north diagonal and
west-east diagonal).
![[reduced bend sinister flag]](../images/v/vxt-d273.gif)
- REEVE
- (v) To thread the halyard through a block (or over a pulley) fitted into the
truck and thereby raise or lower a flag (see also
halyard and
truck).
- REGARDANT
- See Appendix V.
- REGIMENTAL COLOUR (or COLOR)
- See colour 2) and
colours 2).
![[Regimental colour example]](../images/v/vxt-d601.gif)
Regimental Colour 18th Infantry Regiment 18th Century, Germany (fotw)
- REGIMENTAL COLOURS (or COLORS)
- 1) The plural form of regimental colour and in this context used only when
referring to the second or unit flag of more than one battalion/regiment (see
colour 2),
colours 2) and following note).
- 2) In British army usage, those shades or colours that are considered
representative of a particular regiment, and which are usually employed on their
arm flash, camp flag and regimental ties etc., in addition to the formal regimental colour as
defined in colour 2),
colours 2) and in 1) above (see also
camp flag and
fanion 2)).
- REGIMENTAL FLAG
- See 'camp flag'.
- REGISTRATION FLAGS/PENNANTS
- In French maritime usage the term, now obsolete, for those flags/pennants which
were flown from the main masthead of merchant vessels to show in which sector of an
arrondissement maritime (maritime province) or colonial area they were registered,
and in use from 1817 c1929 ¬ arrondissement or sector flags/pennants
(see also main,
masthead and
pennant 2)).
![[registration flag example]](../images/v/vxt-d509.gif)
Registration Flag, One Sector of the Arrondissement of Brest, France (fotw)
Please note, it has been suggested that this type of flag/pennant may have had
wider European usage than is indicated above, however, no further information
can be confirmed at the present time.
- REGULAR CROSS
- See cross 1).
- REICHSKRIEGSFLAGGE
- See war flag 1) and
war flag 2).
- RELIGIOUS BANNER
- See banner 3),
gonfalon 1) and
religious flag.
- RELIGIOUS FLAG
- Generically, any flag that is used in religious worship, or that represents
a particular faith or denomination within that faith (see note below and also
banner 3),
Christian flag,
church flag 2),
dhvaja,
ex-voto flag,
khanda,
prayer flag and
thangka).
Please note that a Roman Catholic church often flies either the flag of the Vatican City State
or a bicolour in the Papal colours of white and gold, that an Islamic mosque usually displays one or more crescent
vexilloids and a Jewish synagogue the Menorah or the Magen David
(see also crescent,
Magen David,
Menorah and
vexilloid). It should be noted also, that religious flags in the US
are often displayed within the church building as well as outside, whereas in the UK Christian churches,
with the exception of those religious banners carried in procession (and laid up military colours), usually
(but not invariably) fly such flags outdoors.





![[radiating flags]](../images/v/vxt-d263.gif)
![[radiating flags]](../images/v/vxt-d263a.gif)
![[radiating flags]](../images/v/vxt-d263b.gif)
![[radiating flags]](../images/v/vxt-d263c.gif)
![[radiating flags]](../images/v/vxt-d263d.gif)


![[Federal Service Flag of Germany]](../images/v/vxt-d411.gif)
![[rank flags]](../images/v/vxt-d267.gif)




![[British Red Ensign]](../images/v/vxt-d270.gif)
![[British Red Ensign]](../images/v/vxt-d270a.gif)
![[British Red Ensign]](../images/v/vxt-d270b.gif)


![[Danger flag, Flag Bravo and Soviet Union]](../images/v/vxt-d1701.gif)
![[Regimental colour example]](../images/v/vxt-d601.gif)
![[registration flag example]](../images/v/vxt-d509.gif)
![[Raven flag]](../images/v/vxt-d269.gif)




![[Royal Dart Yacht Club]](../images/v/vxt-d270c.gif)
![[reduced bend flag]](../images/v/vxt-d271.gif)
![[reduced bend sinister flag]](../images/v/vxt-d273.gif)