![[Samos (incorrect version)]](../images/g/gr_sampa.gif)
Last modified: 2006-05-27 by ivan sache
Keywords: samos | cross (white) | cross (red) |
Links: FOTW homepage |
search |
disclaimer and copyright |
write us |
mirrors
See also:
Other site of interest:
Samos (33,039 inhabitants; 472.5 sq. km) is an island located off the western coast of Turkey. The island is mostly known for its sweet wines.
Ivan Sache, 2 February 2005
The Greeks rebells controlled Samos during the
independence war, but it was returned to
the Ottoman Empire in 1830, with special
conditions. The Principality of Samos was created in December 1832,
under Ottoman sovereignty. It lived in peace until 1908,
when the islanders revolted against Turkey. Prince Andrew Kopasis
followed an anti-Greek policy and was murdered on 22 May 1912.
His successor, Gregory Vegleris, was pro-Greek.
In May 1912, Turkey withdrew its army from the island when the war against Italy
broke out and in September the Greek islanders, led by Themistocles
Sofoules, revolted again. Vegleris escaped and on 24
November 1912 the island was incorporated to Greece.
In 1925 there was a conflict and there was some discussion about the
proclamation of the independence of the island, but nothing
happened.
Jaume Ollé, 26 September 1996
Quoting the Vathi website:
Themistocles Sofoules is one of the most eminent personalities of Samos, during the last twelve-year period of the Principality. (...) In September 1912, Samos revolted under his leadership and on 11 November 1912 the island's national assembly declared its union with "the free Greek Kingdom".
The union was formally established in March, 1913. For two years, until 1914, the Temporary Government of Samos ruled the island, having Themistocles Sofoules as President. From that moment on, Samos became an integral part of the Greek state.
Jan Mertens, 2 January 2004
The flag of the fleet from Samos is blue with a red border. At bottom is a red crescent, pointing downward. Atop the crescent is a red cross in the middle, a red spear on the right. To the left of the cross is a yellow coiled snake. In the upper left corner is a white boat anchor.
According to the Naval Museum of Hania (Crete), the cross stands for Christendom (Greece), the crescent for Islam (Turkey), the snake for wisdom, knowledge and reason, the anchor for stability, the spear for power and the bird for the help from God.
The combination of these elements probably represents the resurrection of the Greek
nation: the cross overpowers the crescent moon. To bring about a
successful fight however power (the spear) was required, as well as
stability and perseverance (anchor), knowledge and wisdom (snake),
and God's help through faith and religion (bird).
The book Hellenic flags [kok97] explains that the flag of the fleet from Samos knew several variants, still with the same elements, cross, crescent, etc... The bird is in fact an owl biting the tongue of the snake. The red border symbolizes the blood of the Turks, the anchor the hope for the successful outcome of the cause, the cross stands for faith in justice and the owl for prudence. Of course various interpretations of these elements exist and have existed.
Bruce Tindall & Pascal Vagnat, 11 January 1999
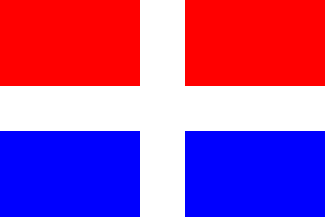
Flag of the Principality of Samos - Image by Herman De Wael, 26 September 1996
The book Hellenic flags [kok97] shows the flag of the Principality of Samos, officially used from 1834 to 24 November 1912, as divided by a white cross, with red upper quarters and blue lower quarters.
Pascal Vagnat, 11 January 1999
The German flag chart Die Flaggen der Kriegs- und Handels- Marinen aller Staaten der Erde (The flags of the navies and merchant navies of all the states of the world, Moritz Rühl, Leipzig, 9th edition, no year given but showing the flag of French president Emile Loubet, 1899-1906) labels this flag Handelsflagge (civil ensign).
Jan Mertens, 22 December 2003
Other reported flag of the Principality of Samos - Image by Željko Heimer, 22 December 2003
A red over blue flag with a small white cross near the hoist is shown as the flag of Samos by Lloyd's House Flags and Funnels, 1911 [llo11], available online on the Mystic Seaport Library website.
Ned Smith, 22 December 2003
The aforementioned German flag chart Die Flaggen der Kriegs- und Handels- Marinen aller Staaten der Erde shows this flag as Staatsflagge (state flag), but with the cross as thick as on the "civil ensign".
Jan Mertens, 22 December 2003
Standard of the Prince of Samos
Left, after Hellenic flags
[kok97] - Image by Pascal Vagnat, 11 January 1999
Right, after Fezvi Kurtoglu [kur92] - Image by Jaume Ollé, 8 October 1996
The standard of the Prince of Samos was blue with in the center a triangle charged with a Greek cross. Some sources says that the triangle is white and the cross red, whereas other sources show a red triangle and a white cross.
Jaume Ollé & Pascal Vagnat, 11 January 1999
On a Samos website, the two images on top show the island's flag and the princely flag held by a policeman. The last image on the sixth row (inauguration of horse tram, 1905) shows the island's flag together with the princely flag. If we compare the various hues on these flags, may we not conclude that the cross-bearing triangle was indeed white?
The aforementioned German flag chart Die Flaggen der Kriegs- und Handels- Marinen aller Staaten der Erde shows the Prince's standard as a blue flag with a white triangle charged with a red cross, the cross being much smaller than on the image shown above.
Jan Mertens, 2 January 2004